Manage Hyper-V Integration Services
Hyper-V Integration Services allow a virtual machine to communicate with the Hyper-V host. Many of these services are conveniences, such as guest file copy, while others are important to the virtual machine's ability to function correctly, such as time synchronization. This set of services are sometimes referred to as integration components.+
For details about each integration service, see Hyper-V Integration Services.+
Important
Each service you want to use must be enabled in both the host and guest so they can communicate. All integration services are on by default on Windows guest operating systems, but you can turned them off individually. The next sections show you how.+
Turn an integration service on or off using Hyper-V Manager
From the center pane, right-click the virtual machine and click Settings.
From the left pane of the Settings window, under Management, click Integration Services.
- +
The Integration Services pane lists all integration services available on the Hyper-V host, and whether they're turned on in the virtual machine. To get the version information for a guest operating system, log on to the guest operating system, open a command prompt, and run this command:+
REG QUERY "HKLM\Software\Microsoft\Virtual Machine\Auto" /v IntegrationServicesVersion
Turn an integration service on or off for a Windows guest
All integration services are on by default on Windows guest operating systems, but you can turned them off individually. The next section shows you how.+
Use Windows PowerShell to turn a integration service on or off
To do this in PowerShell, use Enable-VMIntegrationService and Disable-VMIntegrationService.+
The following examples show you how turn an integration service on and off by doing this for the guest file copy service on a virtual machine named "demovm".+
-
Get a list of running integration services:
PowerShell
Get-VMIntegrationService -VMName "DemoVM" -
The output should look like this:
PowerShell
VMName Name Enabled PrimaryStatusDescription SecondaryStatusDescription ------ ---- ------- ------------------------ -------------------------- DemoVM Guest Service Interface False OK DemoVM Heartbeat True OK OK DemoVM Key-Value Pair Exchange True OK DemoVM Shutdown True OK DemoVM Time Synchronization True OK DemoVM VSS True OK -
Turn on Guest Service Interface:
PowerShell
Enable-VMIntegrationService -VMName "DemoVM" -Name "Guest Service Interface" -
Verify that Guest Service Interface is enabled:
Get-VMIntegrationService -VMName "DemoVM" -
Turn off Guest Service Interface:
Disable-VMIntegrationService -VMName "DemoVM" -Name "Guest Service Interface" - +
Start and stop an integration service from a Windows Guest
Important
Stopping an integration service may severely affect the host's ability to manage your virtual machine. To work correctly, each integration service you want to use must be enabled on both the host and guest.+
Each integration service is listed as a service in Windows. To turn an integration service on or off from inside the virtual machine, you'll start or stop the service.+
Use Windows Services
-
Open Services manager
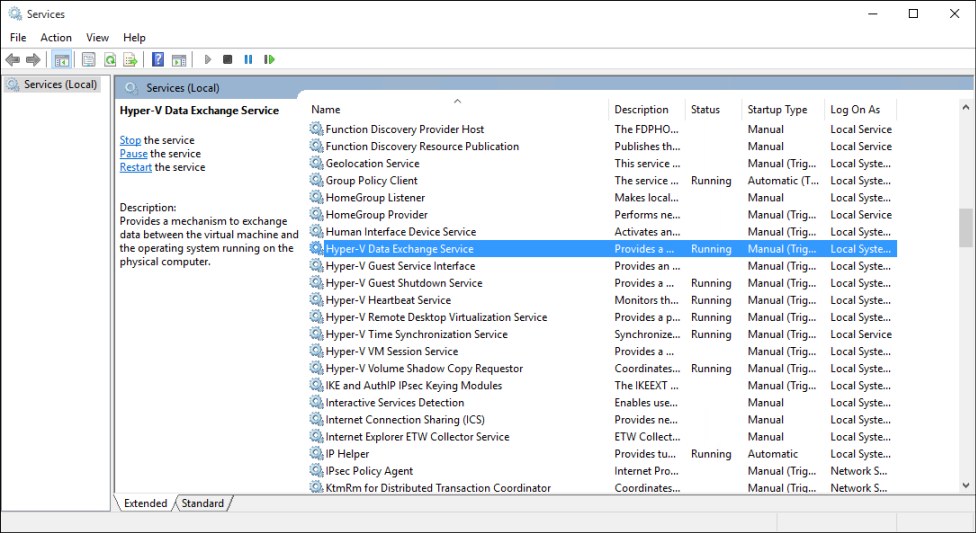
Find the services with Hyper-V in the name.
Right-click the service you want start or stop.
- +
Use Windows PowerShell
-
To get a list of integration services, run:
Get-Service -Name vm* -
The output should look similar to this:
PowerShell
Status Name DisplayName ------ ---- ----------- Running vmicguestinterface Hyper-V Guest Service Interface Running vmicheartbeat Hyper-V Heartbeat Service Running vmickvpexchange Hyper-V Data Exchange Service Running vmicrdv Hyper-V Remote Desktop Virtualizati... Running vmicshutdown Hyper-V Guest Shutdown Service Running vmictimesync Hyper-V Time Synchronization Service Stopped vmicvmsession Hyper-V VM Session Service Running vmicvss Hyper-V Volume Shadow Copy Requestor -
Run either Start-Service or Stop-Service. For example, to turn off Windows PowerShell Direct, run:
Stop-Service -Name vmicvmsession - +
Start and stop an integration service from a Linux guest
Linux integration services are generally provided through the Linux kernel. The Linux integration services driver is named hv_utils.+
-
To find out if hv_utils is loaded, use this command:
BASH
lsmod | grep hv_utils -
The output should look similar to this:
BASH
Module Size Used by hv_utils 20480 0 hv_vmbus 61440 8 hv_balloon,hyperv_keyboard,hv_netvsc,hid_hyperv,hv_utils,hyperv_fb,hv_storvsc -
To find out if the required daemons are running, use this command.
BASH
ps -ef | grep hv -
The output should look similar to this:
BASH
root 236 2 0 Jul11 ? 00:00:00 [hv_vmbus_con] root 237 2 0 Jul11 ? 00:00:00 [hv_vmbus_ctl] ... root 252 2 0 Jul11 ? 00:00:00 [hv_vmbus_ctl] root 1286 1 0 Jul11 ? 00:01:11 /usr/lib/linux-tools/3.13.0-32-generic/hv_kvp_daemon root 9333 1 0 Oct12 ? 00:00:00 /usr/lib/linux-tools/3.13.0-32-generic/hv_kvp_daemon root 9365 1 0 Oct12 ? 00:00:00 /usr/lib/linux-tools/3.13.0-32-generic/hv_vss_daemon scooley 43774 43755 0 21:20 pts/0 00:00:00 grep --color=auto hv -
To see what daemons are available, run:
BASH
compgen -c hv_ -
The output should look similar to this:
BASH
hv_vss_daemon hv_get_dhcp_info hv_get_dns_info hv_set_ifconfig hv_kvp_daemon hv_fcopy_daemonIntegration service daemons that might be listed include the following. If they're not, they might not be supported on your system or they might not be installed. Find details, see Supported Linux and FreeBSD virtual machines for Hyper-V on Windows.
- hv_vss_daemon: This daemon is required to create live Linux virtual machine backups.
- hv_kvp_daemon: This daemon allows setting and querying intrinsic and extrinsic key value pairs.
- hv_fcopy_daemon: This daemon implements a file copying service between the host and guest.
- +
Examples
These examples stop and start the KVP daemon, named hv_kvp_daemon.+
-
Use the process ID (PID) to stop the daemon's process. To find the PID, look at the second column of the output, or use
pidof. Hyper-V daemons run as root, so you'll need root permissions.BASH
sudo kill -15 `pidof hv_kvp_daemon` -
To verify that all
hv_kvp_daemonprocess are gone, run:ps -ef | hv -
To start the daemon again, run the daemon as root:
BASH
sudo hv_kvp_daemon -
To verify that the
hv_kvp_daemonprocess is listed with a new process ID, run:ps -ef | hv - +
Keep integration services up to date
We recommend that you keep integration services up to date to get the best performance and most recent features for your virtual machines. This happens in Windows Server 2016 and Windows 10 by default when your virtual machines are set up to get important updates from Windows Update.+
For virtual machines running on Windows 10 hosts:+
Note
The image file vmguest.iso isn't included with Hyper-V on Windows 10 because it's no longer needed.+
| Guest | Update mechanism | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Windows 10 | Windows Update | |
| Windows 8.1 | Windows Update | |
| Windows 8 | Windows Update | Requires the Data Exchange integration service.* |
| Windows 7 | Windows Update | Requires the Data Exchange integration service.* |
| Windows Vista (SP 2) | Windows Update | Requires the Data Exchange integration service.* |
| - | ||
| Windows Server 2012 R2 | Windows Update | |
| Windows Server 2012 | Windows Update | Requires the Data Exchange integration service.* |
| Windows Server 2008 R2 (SP 1) | Windows Update | Requires the Data Exchange integration service.* |
| Windows Server 2008 (SP 2) | Windows Update | Extended support only in Windows Server 2016 (read more). |
| Windows Home Server 2011 | Windows Update | Will not be supported in Windows Server 2016 (read more). |
| Windows Small Business Server 2011 | Windows Update | Not under mainstream support (read more). |
| - | ||
| Linux guests | package manager | Integration services for Linux are built into the distro but there may be optional updates available. ******** |
* If the Data Exchange integration service can't be enabled, the integration services for these guests are available from the Download Center as a cabinet (cab) file. Instructions for applying a cab are available in this blog post.+
For virtual machines running on Windows 8.1 hosts:+
| Guest | Update mechanism | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Windows 10 | Windows Update | |
| Windows 8.1 | Windows Update | |
| Windows 8 | Integration Services disk | See instructions, below. |
| Windows 7 | Integration Services disk | See instructions, below. |
| Windows Vista (SP 2) | Integration Services disk | See instructions, below. |
| Windows XP (SP 2, SP 3) | Integration Services disk | See instructions, below. |
| - | ||
| Windows Server 2012 R2 | Windows Update | |
| Windows Server 2012 | Integration Services disk | See instructions, below. |
| Windows Server 2008 R2 | Integration Services disk | See instructions, below. |
| Windows Server 2008 (SP 2) | Integration Services disk | See instructions, below. |
| Windows Home Server 2011 | Integration Services disk | See instructions, below. |
| Windows Small Business Server 2011 | Integration Services disk | See instructions, below. |
| Windows Server 2003 R2 (SP 2) | Integration Services disk | See instructions, below. |
| Windows Server 2003 (SP 2) | Integration Services disk | See instructions, below. |
| - | ||
| Linux guests | package manager | Integration services for Linux are built into the distro but there may be optional updates available. ** |
For virtual machines running on Windows 8 hosts:+
| Guest | Update mechanism | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Windows 8.1 | Windows Update | |
| Windows 8 | Integration Services disk | See instructions, below. |
| Windows 7 | Integration Services disk | See instructions, below. |
| Windows Vista (SP 2) | Integration Services disk | See instructions, below. |
| Windows XP (SP 2, SP 3) | Integration Services disk | See instructions, below. |
| - | ||
| Windows Server 2012 R2 | Windows Update | |
| Windows Server 2012 | Integration Services disk | See instructions, below. |
| Windows Server 2008 R2 | Integration Services disk | See instructions, below. |
| Windows Server 2008 (SP 2) | Integration Services disk | See instructions, below. |
| Windows Home Server 2011 | Integration Services disk | See instructions, below. |
| Windows Small Business Server 2011 | Integration Services disk | See instructions, below. |
| Windows Server 2003 R2 (SP 2) | Integration Services disk | See instructions, below. |
| Windows Server 2003 (SP 2) | Integration Services disk | See instructions, below. |
| - | ||
| Linux guests | package manager | Integration services for Linux are built into the distro but there may be optional updates available. ** |
For more details about Linux guests, see Supported Linux and FreeBSD virtual machines for Hyper-V on Windows.+
Install or update integration services
For hosts earlier than Windows Server 2016 and Windows 10, you'll need to manually instructions from the guest operating system. These steps can't be automated or done within a Windows PowerShell session.+
Open Hyper-V Manager. From the Tools menu of Server Manager, click Hyper-V Manager.
Connect to the virtual machine. Right-click the virtual machine and click Connect.
From the Action menu of Virtual Machine Connection, click Insert Integration Services Setup Disk. This action loads the setup disk in the virtual DVD drive. Depending on the guest operating system, you might need to start the installation manually.
After the installation finishes, all integration services are available for use.
Original Article:
